Description
Gold ore dressing is a comprehensive process that involves multiple stages, from extracting gold from ore to refining it into pure gold. Among the key components in this process is the Electric Gold Melting Furnace, an essential tool in the final smelting stages. This introduction outlines the role of electric melting furnaces in combination with desorption electrolytic systems and traditional roasting smelting methods, highlighting their efficiency, environmental benefits, and technological features.
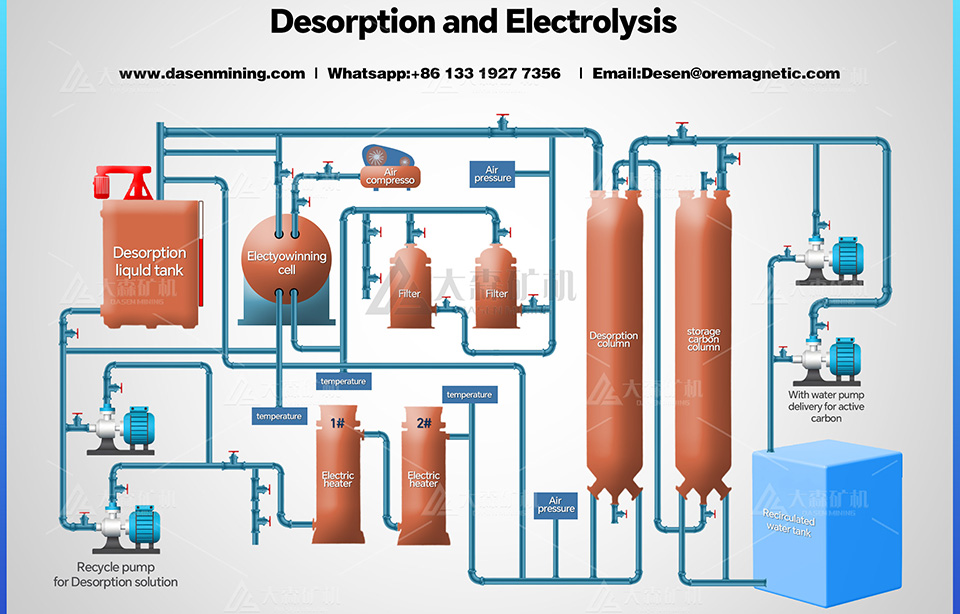
1. Desorption Electrolytic + Smelting System
The high temperature and high pressure desorption electrolysis system is a modern approach to extracting gold from gold-loaded carbon. It works by desorbing and electrowinning gold under controlled thermal and pressure conditions.
System Components:
- Desorption Column
- Electrolytic Cell
- Circulating Pump
- Electric Heater
- Filter
- Air Compressor
- Desorption Liquid Tank
- Control Cabinet
Key Features:
Fast Processing
- The system completes a full desorption cycle in 12–14 hours, approximately three times faster than conventional methods.
Cyanide-Free, Eco-Friendly Operation
- Utilizes sodium hydroxide instead of sodium cyanide, reducing environmental impact and operational costs.
- Lower energy consumption: Power usage is only ¼ to ½ of traditional systems due to improved heat preservation and process speed.
Automated Control
- Equipped with an automated control system for precise operations and reduced human intervention.
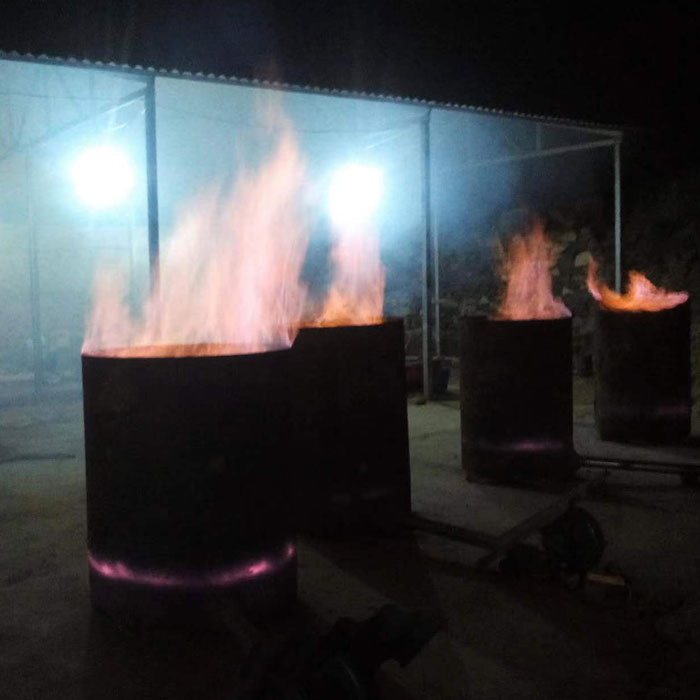
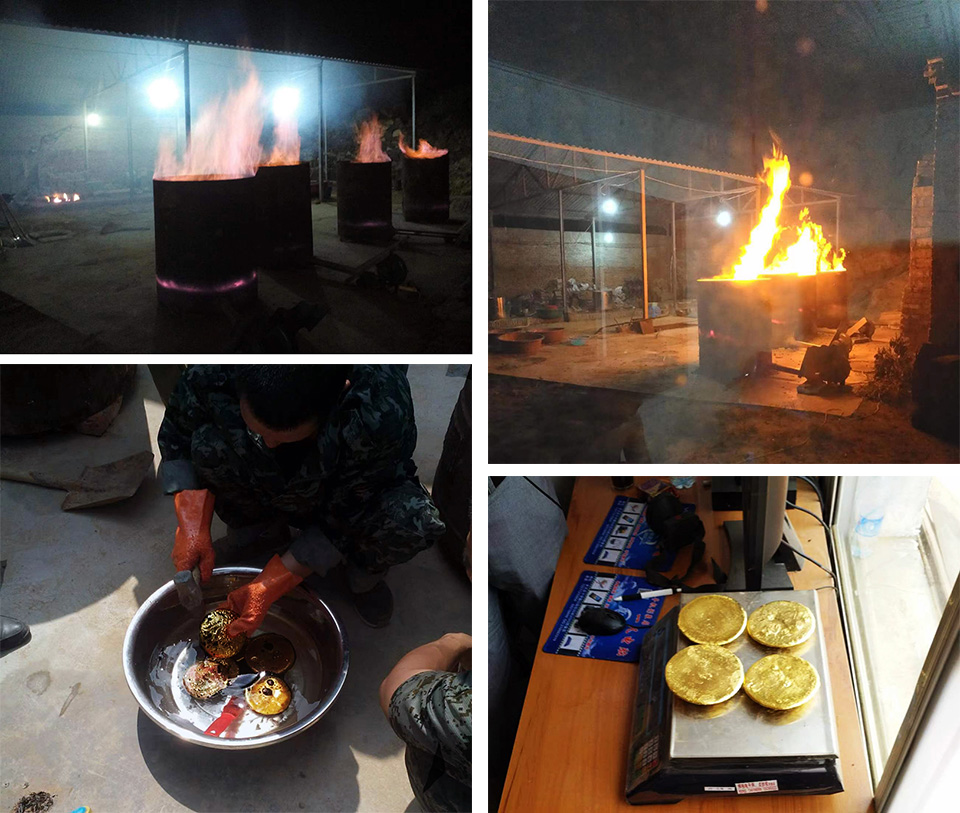
2: Roasting gold-loaded carbon for smelting
It is traditional way to get the final pure gold. The materials needed are refractory brick, metallic lead(Electrolytic lead), coke, blower, activated carbon combustion drum, cooling crucible, graphite crucible, stainless steel, etc.
The operation procedures as below:
1. Burining the gold-loaded carbon
2. The carbon slag is crushed after cooling, then add pure lead and borax, and mix well.
3. The uniformly stirred carbon slag is put into a crucible and calcined
4. After calcining for 1-2 hours, the carbon residue is dissolved into a liquid and stirred as water, then take out the furnace for cooling . After cooling, the carbon residue is poured out. At this time, gold and lead have settled into the bottom of the pot and knocked out and are available.
5. Removing lead. Put the lead-containing gold in a cement-filled cauldron, put coal balls or coke on it, blow it with a fan, and then stop blowing to let it naturally rise to more than 1300 degrees. At this time, the lead will vaporize and evaporate. This process takes 2-3 hours.
6. The refinement step is after removing lead. After removing lead, obtain gold with low purity, add silver (preferred) or lead to melt, so that the alloy reaches 15% -25% gold content, and then slowly drop into a large amount of cooling water to make the alloy into small particles, which is beneficial to achieve a good reaction with nitric acid, replace nitric acid continuously with new ones to remove silver and lead, and finally obtain high-purity gold powder. After removing moisture, melt into a ceramic crucible to obtain a gold ingot.
2. Traditional Roasting Gold-Loaded Carbon for Smelting
While modern systems are efficient, the traditional roasting method remains in use for extracting high-purity gold. This method involves thermal processing of carbon residues and smelting with lead.
Required Materials:
- Refractory bricks
- Electrolytic lead
- Coke
- Blower
- Activated carbon combustion drum
- Cooling and graphite crucibles
- Stainless steel tools
Process Overview:
Step 1: Carbon Combustion
- Burn gold-loaded carbon in a combustion drum.
Step 2: Crushing and Mixing
- Crush the carbon slag, mix with pure lead and borax.
Step 3: Smelting
- Smelt the mixture in a crucible at high temperatures for 1–2 hours.
Step 4: Cooling and Separation
- After smelting, allow the mixture to cool. Gold and lead settle at the bottom for collection.
Step 5: Lead Removal
- Heat the lead-gold alloy above 1300°C using coal or coke to vaporize the lead.
Step 6: Refinement
- Add silver or lead to form a gold alloy (15–25% gold), then drop into water to granulate.
- Use nitric acid to dissolve other metals and obtain high-purity gold powder.
- Final melting in a ceramic crucible produces gold ingots.

Application of Electric Gold Melting Furnaces
Whether used in conjunction with electrolytic desorption systems or traditional smelting, electric gold melting furnaces play a pivotal role in:
- Final gold smelting and refining
- Maintaining consistent high temperatures
- Ensuring energy-efficient and controlled melting processes
- Producing high-purity gold ingots ready for the market
Whatsapp:+8613319277356
Email: chemicals@dasenmining.com




